
With the truth, all given facts harmonize; but with what is false, the truth soon hits a wrong note
Aristototle
Premise 1: Matter is not eternal and chance cannot be a first cause
The Law Of Cause And Effect is a universal law which specifically states:
- Every single action in the universe produces a reaction no matter what.
- Every single effect within our world and upon the earth has a cause and an original starting point.
If you search “Formation and Evolution of the Solar System” on Wikipedia it states: “The solar system began 4.5 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the sun, while the rest flattened…of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small bodies formed.”
Wikipedia describes the Big Bang but it doesn’t provide the “cause ” of any of the components within their description of the event such as:
- The gravitational collapse
- The giant molecular cloud
- The collapsing mass
? ← (molecular cloud, mass) ← Universe ← Everything
Science has verifiable proofs for the causes of some of the most complex realities of the universe. For example gravity, photosynthesis, black holes or radio waves. The root cause of all of these phenomena has either been verified through direct observation or by mathematics.
If evolutionist are scientifically honest they will have to admit they don’t have an answer as to what caused the Big Bang or any of the components of the Big Bang Wikipedia mentions that can be verified scientifically.
Verified Science always provides the what, how, and why…Evolution only provides the what
The Law of First Cause implies by extension that : That if there is matter and energy it had to originate from somewhere, and it had to be caused by something.
Any explanation of the Origin of the Universe has to meet the standards of The Law of Causation and Effect. The Big Bang cannot be considered a scientific fact and be exempt from the conditions of this law at the same time. Here are those conditions:
A. Anything that begins to exist has a cause
B. The Universe began to exist
C. Therefore the Universe has to have a First Cause
Evolutionist fully realize that the law of cause and effect has to be adhered to in order for the theory to be seen as legitimate science but in the absence of being able to find a provable cause that can be observed, tested and verified they have developed theories within the theory.
What about Chance as the cause?
In the absence of a scientifically verifiable “Cause Agent” for the Big Bang modern science has defaulted to “chance” as the primary cause of the Big Bang and the commencement of evolution.
Evolutionary biology since Darwin has seen a dramatic entrenchment and elaboration of the role of chance in evolution. It is nearly impossible to discuss contemporary evolutionary theory in any depth at all without making reference to at least some concept of “chance” or “randomness.”
Grant Ramsey and Charles H. Pence, University Press Scholarship Online
What the word “Chance” really means:
Chance: a: the possibility of a particular outcome in an uncertain situation (What chance has he of pulling through?)
Merriam Webster Dictionary
b: the degree or likelihood of such an outcome (The project had a small chance of success.)
c: how something happens unpredictably without discernible human intention or observable cause
If chance is defined as something without an observable cause how can “chance” be a cause? Chance means to happen by luck or fortune. It doesn’t have any scientific standing to be declared the cause of anything.
Evolutionist count on people gliding over the fact that they are ascribing power and force to a word that should only be used to describe probability—in doing so they have felt free use it as a vague, unprovable, fill in the blank cause agent for the formation of the universe and evolution on earth.
Here are examples of how evolutionist inject the word Chance with creative power:
Chance alone is the source of every innovation. Chance alone is the source of all creation in the biosphere
Jacques Monod; Nobel Prize winning Biologist
Nature, according to Darwin, was the product of blind chance and a blind struggle, and man, a lonely intelligent mutation, scrambling with the brutes for his sustenance
J.W. Burrow; Historian Cambridge University, Introduction to The Origin of Species
“One has only to wait: time itself performs the miracles. Given so much time the impossible becomes possible, the possible probable, and the probable actually certain.”
Gerald Wald; Nobel Prize winning Physiologist
Two primary reasons chance has been chosen by Evolutionist to be the “cause of the Universe”
- Science declares every effect has to have a cause, the cause of the Big Bang has not been able to be scientifically proven so unprovable “chance” has been adopted and promoted as the cause.
- Chance as a cause also provides a stop gap answer to the question “Why hasn’t life formed on other planets if they were all formed at the same time and from the same matter used in the Big Bang. Is the reason because they didn’t have “”Chance” but the Earth did?
Three reasons why chance cannot be the “cause of the universe”
1. Chance is neither a force, energy, object, or matter which a cause would have to be
Oxford Dictionary defines the word Cause as:
A person or thing that gives rise to an action, phenomenon, or condition
Chance is neither matter, energy, or an observable force therefore it could never be the cause of anything.
When scientists attribute instrumental power to chance—they have left the domain of reason, they have left the domain of science; they have turned to pulling rabbits out of hats, they have turned to fantasy. All scientific investigation becomes chaotic and absurd, because it can’t really yield what it should yield, because they won’t allow it to.
John MacArthur; Creation Believe It or Not
2. Chance as a causal force cannot be measured, tested or quantified (chance+nothing=everything?)
ver·i·fy
/ˈverəˌfī/ verb
make sure or demonstrate that (something) is true, accurate, or justified.
“his conclusions have been verified by later experiments”
Oxford Dictionary
Chance by definition is just a description of unpredictability it cannot be a person or thing that gives rise to an action, phenomenon, or condition as the definition of what a “cause” is states. Closer examination of the word chance reveals that it is not a thing, but describes something else. A cause has to be either a force (energy) or matter of which chance is neither. Since chance is not a force or matter it can’t be quantified, measured or tested scientifically.
Big Bang Cosmology, and Evolution are the only scientific theories, hypothesis or published explanation where “Chance” has been accepted as a verifiable cause agent. Why has this exception been made?
With the failure of these many efforts, science has been left in the somewhat embarrassing position of having to postulate theories of living organisms which it could not demonstrate. After having chided the theologian for his reliance on myth and miracle, science found itself in the inevitable position of having to create mythology of it’s own that somehow something they cannot prove can take place today had, in truth, taken place in the primeval past
Loren Eisley; Anthropologist, The Immense Journey p. 199There can be no doubt that after a century of intensive efforts biologists have failed to validate it in any significant sense. The fact remains that nature has not been reduced to the continuum that the Darwinian model demands, nor has the credibility of chance as the creative agency of life been secured.
Michael Denton; Theory In Crisis, PhD Biochemistry, Senior Fellow Discovery Institute for Science and Culture
3. The odds against complex life forming randomly are too astronomical
An undifferentiated external force (Big Bang) is simply too blunt an instrument to accomplish such a task. Energy might scatter parts around randomly. Energy might sweep parts into an orderly structure such as a vortex or funnel cloud. But energy alone will not assemble a group of parts into a highly differentiated or functionally specified system such as an airplane or cell
Stephen C. Meyer; Ph.D Science Cambridge University; Signature of A Cell p. 257

The chance of obtaining a single functioning protein by chance is comparable to a star system full of blind men solving Rubik’s Cubes simultaneously
Sir Fred Hoyle; Formulated the theory of Stellar Nucleosysynthesis
The more advances science makes in micro-biology, genetics, and physics—the harder advocating “Blind Chance” as the mechanism for the mechanism for the complexity, laws, and precision of the Universe will be
Nothing can come from nothing. If something came from nothing then the nothing has the property of being able to produce something and so the “nothing” is something, a “thing” that can produce what we have today… We need to discover, scientifically, the facts. To say before the “big bang” there was nothing is nonsense. Before the “big bang” (whatever that was) there was something that gave rise to the “big bang” and we are ignorant of what that was.
We need a theory of what gave rise to what we call “the Big Bang”, one that doesn’t assume nothing produced something.
Peter LePort, Surgeon, Ayn Rand Institute Board of Directors
Challenge Question: After careful examination of what “Chance” is by definition should scientist teach that it is the absolute cause of the “Big Bang” and the emergence of life on Earth?
Premise 2: Diversity at the systems level of nature point to a designer and organizer
The theory of evolution posits that chance, matter and energy alone have given rise to all things including biological systems. If the theory is true— then all of the information found in DNA, the Laws of Physics, and the mathematical precision of the universe arose spontaneously through the blind interaction of matter and energy.
Charles Darwin had no idea that DNA was responsible for the development, growth, reproduction, and functionality of everything that is alive on the earth. Not only does every living thing have DNA as its blueprint, but every single cell, in every single living thing does too. This is why their is not only tremendous diversity between species, but their is tremendous diversity within species.
How many living things that have their own DNA code are there you ask?
Biodiversity is a term used to describe the enormous variety of life on Earth. Biodiversity refers to every living thing, including plants, bacteria, animals, and humans. Scientists have estimated that there are around 8.7 million species of plants and animals in existence. However, only around 1.2 million species have been identified and described so far, most of which are insects. This means that millions of other organisms remain a complete mystery. National Geographic
Biodiversity means that their 8.7 million living things with different DNA coding that causes them to have such different physical traits, reproductive systems, instincts, etc. to the extent they have to be classified and catalogued separately. This classification is called Taxonomy.
There are 8 super systems of taxonomy that include countless biologically and genetically distinct subsystems to numerous to list. Below is a basic taxonomical chart that is by no means comprehensive:
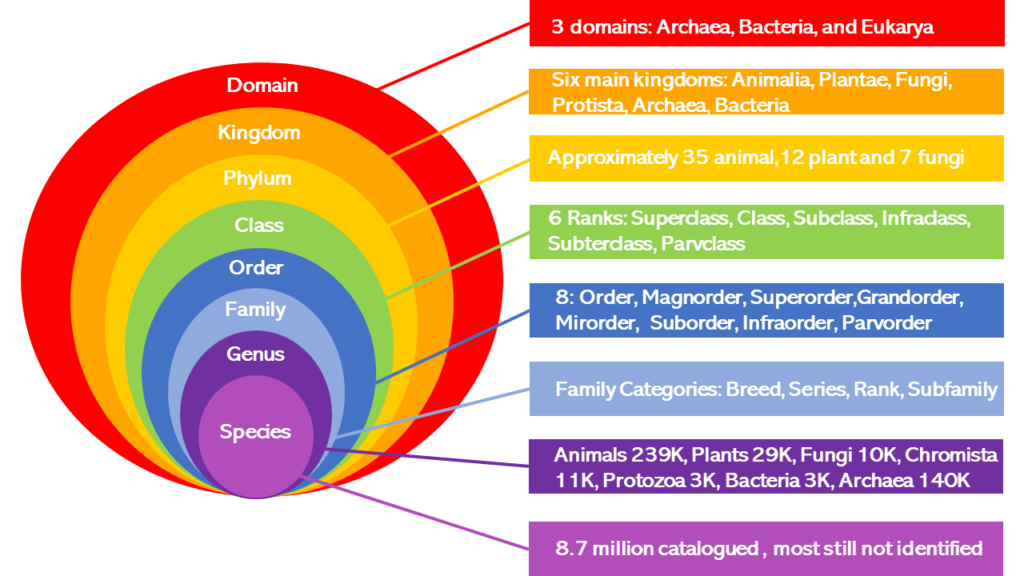
Evolution demands that all of this systematic biodiversity originated randomly by chance, and that all species are evolutionary descendants of each other. Yet there are so many distinct classes, orders, genus, and species that cannot be reconciled as ancestors genetically.
Their is so much genetic diversity that science has developed several global databases in order to properly categorize their specific DNA. Here is a list of International Taxonomic Organizations:
| Names Of International Taxonomic Information Organizations and Systems |
| International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses |
| International Institute for Species Exploration |
| International Botanical Congress |
| All Species Foundation |
| World Register of Marine Species |
| Global Biodiversity Information Facility |
| Barcode of Life Data System |
| Integrated Taxonomic Information System |
| International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants |
| Consortium of European Taxonomic Facilities |
| International Association for Plant Taxonomy |
| International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature |
| Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission |
| World Register of Marine Species |
The earth’s biodiversity is so vast that these listed Taxonomical Organizations and science as a whole have not been able to keep up with classifying species. Biologist believe that 86 percent of the worlds species are still waiting to be found and classified.
It is a remarkable testament to humanity’s narcissism that we know the number of books in the US Library of Congress on 1 February 2011 was 22,194,656, but cannot tell you – to within an order of magnitude – how many distinct species of plants and animals we share our world with
Lord Robert May: Royal Society President PLOS Biology
Biologist and Taxonomist believe there are still over 7 million more species that need to be classified according to genetic similarities. That means the remaining 7 million will be:
- Genetically distinct from each other
- Have different physical and morphological attributes from each other
- All be reproductively isolated
- Have different communal behaviors and instincts
Challenge Question: Did you ever imagine that in the 21st century scientist would only have 20% of living species classified?
Premise 3: Where did the information bio-diversity reveals come from?
Evolutionist believe that all of this beauty, design, order and genetic diversity is simply the product of an undirected process such as natural selection acting on random variations
ran·dom
/ˈrandəm/
adjective
1.
made, done, happening, or chosen without method or conscious decision.
The words random and complexity are contradictions in terms. The main tenets of Information Theory or The Laws of Information are:
- Information and intelligence cannot arise randomly but must have an agent
- Irreducibly complex design does not arise randomly but must have an designer
Each of the 8.7 million known species scientist believe live on the earth will sooner or later be catalogued according to strict taxonomic guidelines that include biological and behavioral traits such as hive building by bees, or ant slavery etc., migration, hibernation all of which are determined and controlled by each species distinct and incredibly comprehensive coded DNA. This amounts to an incalculable amount of data.
In order to estimate how much information DNA can store—A team at Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and Harvard Medical School (HMS) has developed a low-cost DNA storage technique that enables encoding digital information at large scale. Nature Communications.
They estimated that one gram of DNA can hold 215 petabytes or 1 million gigabytes. They wrote that assuming the Avengers Endgame movie contained 6 gigabytes of information—then you would be able to store 36 million copies of the movie in one gram of DNA. One human has 20 grams or 720 million copies of Avengers Endgame’s worth of information.
Now try and calculate the amount of information the DNA of 8.7 million species contain. Where did this information come from and how did it organize itself randomly?
We don’t have a single example in the history of science in which information has ever come from anything other than intelligence. There is no property of physics or chemistry that can account for the information we see in DNA
Stephen C. Meyer; Cambridge Philosopher of Science
Richard Dawkins a evolutionary biologist maybe the world’s leading proponent of evolution admits that information, design, and complexity arising by chance is difficult to impossible to explain.
We have seen that living things are too improbable and too beautifully “designed” to have come into existence by chance
Richard Dawkins; The Blind Watchmaker
The sheer numbers of species discovered and still undiscovered, all of which are genetically unrelated demonstrate beauty, imagination, and creative capacity that boggles even the most atheistic and scientific minds. How did this diversity arise by chance?
Challenge Question: Can random processes in nature account for the complexity of genome diversity and systems complexity found in nature?
ThinkCube Truth Veracity Grid
- Have I considered the issue carefully and honestly with an open mind?
- Does what I think conform to the rules of logic and avoid contradictions?
- Are my conclusions free from bias and presuppositions?
