
Premise 1: Modern Genetics has proven that an organism’s DNA prevents it from being able to evolve into another species
On February 28, 1953 Cambridge University scientists James D. Watson and Francis Crick announced the double helix structure of DNA, the molecule containing human genes. James Watson in his book The Double Helix claimed that Crick announced the discovery by walking into the nearby Eagle Pub and blurting out:
“we have found the secret of life.”
“The truth of that statement wasn’t far off, as Watson and Crick had solved a fundamental mystery of science—how it was possible for genetic instructions to be held inside organisms and passed down from generation to generation”
History.com
What do a human, an orchid, or an amoeba have in common? Each of these things—including all other organisms on earth have DNA which are their own molecular instructions for life. Encoded within the DNA are the directions for traits as diverse as the color of a person’s eyes, the scent of an orchid, and even the way a bacteria infects the lung. DNA is found in all living cells and these precise instructions necessarily infer mapping and design.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a molecule that contains the biological instructions that make each species unique.
National Human Genome Research Institute
DNA is a code programmed with the exact information to produce, preserve, and repair that living thing. An animal or plants DNA contains precise instructions that limit what it can be or do. DNA is not an open access code which it would have to be in order for evolution to be true.
DNA is a closed access code that only allows for mutations ( or the rearranging or deletion of existing code). In order for Evolution to be true would require DNA to be open access to allow random additions of information over time.
Modern Genetic research and Reproductive Science has shown that adding information to a species DNA causes system failure. This is the reason Scientist have not been able to create any new species but have only been able to alter the ones that already exist even though they have the intelligence and resources, and have tirelessly attempted to do so.
This gives rise to the question; if Geneticists are not able to reproduce evolution’s results in the laboratory…Then how are we to believe it can happen randomly and at just the right time to create new species, or organs, wings, or eyes?
What Genetics has revealed through such testing is that DNA not only contains the precise instructions that make a species what it is—but it also contains the genetic restraints and boundaries that keep it what it is. These are prohibit a species from being able to be cross breed or change into another species. These limitations are critically necessary in order to keep nature from falling into total confusion.
If DNA was open access code and enabled nature over time to interject additions and deletions to code randomly— then their would be intermediate species (transistionals) which are species that are in the process of becoming something they aren’t already. This would not only make classification of species impossible—but nature’s food chain would be thrown into chaos and all systems of nature would ultimately collapse.
Are Mutations A Viable Mechanism For Evolution?
genetic mutation
noun
pluralgenetic mutations
: a permanent alteration in the nucleotide sequence of one or more genes or in the number or structure of one or more chromosomes
Merriam Webster Dictionary
Charles Darwin’s Theory of Evolution was predicated upon a series of countless favorable micro-mutations occurring just where and when they are required and needed to create complex organs and organisms. Evolutionist believe that because living organisms have the capacity to mutate they can evolve into other more complex organisms over vast periods of time.
To account for the appearance of design Darwinian scientists believe the evolutionary mechanism of mutation and natural selection has the power to mimic a designing intelligence without itself being designed or guides in anyway. However, modern geneticists have revealed that mutations do not have this seemingly miraculous power to produce the new information needed to change one species to another, mutations have been proven to only be able to create changes within a species and most times with harmful results.
Mutations do not change the nature or the kind of any living organism. They can’t make it anything other than it is. What mutations involve is always a loss or mixing of existing information. There is never a gain of information.
When asked if new information can originate in a living organism through mutations—Dr. Werner Gitt; Director and Professor at the German Federal Institute of Physics and Technology replied:
Mutations never add new genetic information; therefore mutations do not work toward an upward evolutionary process, therefore they cannot be the mechanism for evolution.
Mutations can produce new varieties within a species, but even with the advances of modern science breeders and experimenters have not been able to produce entirely new forms of life.
The Lenski experiment is an ongoing study in experimental evolution begun by Richard Lenski at the University of California, Irvine in cooperation with Michigan University, and overseen by Jeff Barrick a the University of Texas. The experiment covers 60,000 generations of E.coli bacteria, the equivelent of 1.5 million years of evolutionary history. Yet for all the mutations observed, there have been no innovations observed that would enable bacteria to produce anything other than bacteria.
living fossil
noun
: an organism (such as a horseshoe crab or a ginkgo tree) that has remained essentially unchanged from earlier geologic times and whose close relatives are usually extinct
Merriam Webster Dictionary
Evolutionist believe that single celled organisms such as an amoeba transformed upwardly to other complex organisms such as mammals, primates, octopus, or bees. Cynobacteria is the oldest living fossil at 3.5 billion years old and it’s DNA is exactly the same today. Living fossils such as turtles, aardvarks, horseshoe crabs, nautilaus, and elephant sharks and numerous other organisms appear in the fossil record as we see them today indicating their historic DNA was the same as their modern DNA.
At the time of his theory Charles Darwin had never even heard of Deoxyribonucleic Acid or that genes even existed much less that genes limit a species to it’s own precise instructions. Charles Darwin had based the potential of mutational evolution on his study of different animal and plant breeder’s ability manipulate physical and behavioral aspects of plants and animals by cross breeding groups within a species.
Although there has been incredible advancement in breeding technology and reproductive biology no one has been able to develop the innovative ability create or change one species into another.
If Charles Darwin had access to the modern research of mutations such as the Lenski Experiment he likely would have abandoned his own theory.
Is it possible that an animal having, for instance, the structure and habits of a bat, could have been formed by the modification of some other animal with widely different habits and structure? Can we believe that natural selection can produce, on the one hand, an organ of trifling importance, such as the tail of a giraffe, which serves as a fly-trapper, and on the other hand, an organ so wonderful as the eye?
On The Origin of Species; Chapter 6 Difficulties Of The Theory
Challenge Question : If you were to stretch the DNA code in one human body all the way out it would be about twice the diameter of the Solar System. Do you think that if Charles Darwin could have had access to the Genome Research we have today that he would still believe an amoeba which has on single cell’s worth of data exclusive to it being an amoeba—could eventually evolve into a human which has over 30 trillion cells worth of data which is totally different than the instructions in a amoeba’s single cell?
Premise 2: Information Theory VS The Theory of Evolution
information
noun in·for·ma·tion ˌin-fər-ˈmā-shən
(1): Intelligence; News (2): Facts; Data
: the attribute inherent in and communicated by one of two or more alternative sequences or arrangements of something (such as nucleotides in DNA or binary digits in a computer program) that produce specific effects
Merriam Webster Dictionary
The Two Basic Tenets of The Laws of Information:
- Information is non-material and cannot be reduced to the interaction of matter and energy.
Example: Imagine a sandy stretch of beach. With my finger I write a number of sentences in the sand. The content of the information can be understood. Now I erase the information by smoothing out the sand. The content of the information can be understood. Now I erase the information by smoothing out the sand. Then I write another sentence in the sand. In doing so I am using the same matter as before to display this information. Despite this erasing and rewriting, displaying and destroying varying amounts of information, the mass of the sand did not altar at any time. The information itself is thus massless.
2. An intelligent sender is the only entity that can produce universal information
In the same way, if you were walking on the beach and found a sentence written on the beach he would naturally assume someone wrote it and not that it just appeared. Design works the same way: If you found a Rolex watch, he could not assume that the watch randomly, and spontaneously designed and formed itself organically without a communicative mind.
All biological systems depend on information storage, transfer, and interpretation for their operation. Some examples include : Cellular, molecular, and brain neuropathy.
Here are three examples of vast information systems that have been operating in the Universe every second of every day since it began
Atomic Physics and Quantum Mechanics
Atoms are called the basic building blocks of matter. Atomic Physics is the scientific study of the structure of the atom, its energy states and its interactions with other particles and electric and magnetic fields.
Atoms are a million times smaller than the thickest human hair. About 5 million hydrogen atoms could fit inside a pin head.
Since the 1970’s the multiple branches of physics research has been trying to estimate the information capacity of the universe. Experts at the science journal AIP used the Shannon Information Theory calculated that each atomic particle in the universe has 1.509 bits of information. They also calculated that the information content of all the matter in the observable universe contains around 6 x 10 followed by 80 zeros. 6 x 100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
The important point of this is not merely that all the information contained in the Universe is incalculable but that all of the multiple branches of physics research realize that every particle (electron, proton, and neurons) contains coded information which are called bits.
There are 15 branches of Quantum Physics (or Quantum Mechanics) which is the field of science charged with describing the behavior of nature at and below the scale of atoms. None of these 15 branches have been able to create a single atom or the information an atom contains. Each branch merely represents specialist charged with discovering new information, or analyzing and interpreting exiting information in that field of atomic research.
Is it incredible to think that each branch would require some of the smartest intellectuals in the world with 12 plus years of intensive academic training to analyze information that supposedly arose randomly and without purpose?
General Physics
General Physics is a branch of science that studies how the how the Universe’s fundamental components interact within the concepts of space, time, energy and force.

Galileo said that the book of nature is written in the language of mathematics. Physics is predominately about the “mathematical information” contained in the Universe.
All of the known Laws of Physics are based on mathematical formulas that explain the certain behaviors in the observable universe
- Law of Cosmic Expansion
- Law of Planetary Motion
- Law of Gravitation
- Law of Motion
- Law of Thermodynamics
- Law of Buoncy
- General Relativity
Math is the way science quantifies, describes, and verifies the information, constants and laws that the Universe operates by.
There are 26 physical constants in the Universe. Examples are the speed of light constant, gravitational constant, gas constant etc. They are mathematical values that have never changed since the beginning of the universe and every atomic particle is designed to work as per the parameters of these constants.
Here are 8 examples of the 26 constants and their mathematical formulas
Electron rest mass me 9.109 × 10−31 kg
Proton rest mass Mp 1.6726 × 10−27 kg
Electronic charge e 1.6022 × 10−19 C
Speed of light in free space c 2.9979 × 108 m s−1
Permeability of free space µ0 4π× 10−7 H m−1
Permittivity of free space 0 8.854 × 10−12 F m−1
Planck’s constant h 6.626 × 10−34 J s
Reduced Planck’s constant h¯ = h/2π 1.0546 × 10−34 J s
There are 15 branches of Physics that use the laws and constants of physics as foundational information to check and confirm all other physical data.
None of them have been able to explain why these constants exist, never change, or how they arranged themselves randomly.
It’s scientifically impossible to explain how 26 constants have remained precisely fixed at their operating values for billions of years. Further, it’s impossible to scientifically explain how every type of subatomic and atomic particle is designed to work as per the parameters of these 26 constants. Every type of sub-atomic particle in this universe has obeyed these 26 parameters since the universe was created. This is nothing but intelligent design
Jeff Miller PhD Molecular Mechanisms. UCLA Dept. Molecular Genetics
Molecular Biology
The Human Genome Institute defines DNA as “a molecule that contains biological instructions that make each species unique” —the word “instructions” is a synonym for information.
DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce. To carry out these functions, DNA sequences must be converted into messages that can be used to produce proteins, which are the complex molecules that do most of the work in our bodies.
DNA much like atomic mass, chemistry, and the Laws of Physics contains coded language of the most sophisticated variety. It also has information storage ability like the atom and it’s isotopes do.
DNA is like a computer program but far, far more advanced than any software ever created
Bill Gates, The Road Ahead
DNA can store 140,000 times more data than iron (III) oxide molecules, which stores information on computer hard drives.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) has the potential to be a sophisticated, stable, and dense information storage medium. DNA has been used by nature for over 3.5 billion years to store genetic instructions for the development, growth, reproduction, and functioning of organisms and viruses. DNA’s four-letter nucleotide code can be used to represent letters, digits, and other characters, similar to the binary digital code used by computers. DNA can also retain information for thousands of years, and has been recovered after being frozen in the tundra for 2 million years.
Wyss Institute; Harvard
Notice that scientist commonly refer to DNA using descriptors such as information storage medium, binary digital code, letters, digits, and characters.
DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce. To carry out these functions, DNA sequences must be converted into messages that can be used to produce proteins, which are the complex molecules that do most of the work in our bodies.
There are 8.7 million classified species in the world and each contain its own set of these specific instructions. Evolutionist believe this information arose randomly, and organized itself into the complexity found throughout the Biosphere.
Assuming that the original primeval form of life was some kind of an ameoba—where did it obtain the almost infinite number of bits of information required to be stored in its DNA storage and retrieval system? In order to transform the ameoba type of cell to a mammal, a primate, an octopus, or a bee, new bits of holistic information are required. neither the primeval ameoba type of cell nor the inorganic matter of which it is constructed contains such highly specialized, holistic information which is necessary to transform the alleged ameoba into, say, an anthropoid ape.
Is it legitimate to assume that such incredible amounts of information arose spontaneously out of thin air by pure chance?
A.E. Wilder-Smith; PhD Physical Organic Chemistry, PhD Pharmacology
The Law of Information dictates that any kind of information much less the hyper-advanced technology found in DNA cannot arise randomly, or by sheer interaction of matter with energy.
The amount of information discovered by science up until now is just a drop in the bucket
Most of the universe that can be known remains unknown. Humans haven’t even explored all the worlds in our solar system, and we have yet to send a space probe to even the nearest of the billions upon billions of other stars in the galaxy. In many ways, we are still novices playing with toy models seeking to understand the stars, and the remaining 95% of the Universe is stuff that we can’t see, and don’t yet understand.
NASA.gov
There are over 30 sub-disciplines of biology— All of which the minimum of a Master or PhD degree is required
| List of Biology Sub-Disciplines | ||||
| Biochemistry | Biophysics | Cell Biology | Biotechnology | Histology |
| Genetics | Molecular Genetics | Classical Genetics | Genomics | Population Genetics |
| Anatomy And Physiology | Animal | Plant | Fungal | Bacterial |
| Microbiology | Virology | Bacteriology | Protozoology | Ornithology |
| Mycology | Horticulture | Mammology | Marine Biology | |
| Botany | Economic Botany | Plant Botany | Brycology | Phycology |
| Zoology | Invertabrate | Etymology | Parasitology | Vertebrate |
| Endoctrinology | Population Ecology | Community Ecology | Terrestrial Ecology | Aquatic Ecology |
| Neurobiology | Physiological Ecology | Behavioral ecology | Environmental Biology | Forestry |
| Neuroscience | Fisheries Biology | Wildlife Biology | Aquaculture | Paleontology |
| Immunology | Immunopathology | Embryology | Sociobiology | |
| Medicine | Pharmacology | Forensics | Toxicology |
All of these Biology disciplines just like every other discipline of physical science represent the information discovery and interpretation mechanism of the known Universe. Science cannot create information it can only discover, interpret and explain the information the Universe contains.
The Universe’s information and discovery potential is as infinite as the number of coded particles in the universe is. Infinite
The theory of evolution asserts that all of the hyper-organized information that the Universe contains is the result of un-directed, random and spontaneous interaction between matter and chemicals.
Spontaneous creation is the reason there is something rather than nothing. Why the Universe exists, Why we exist
Richard Dawkins; The Blind Watchmaker
This explanation defies the Scientific Laws of Information and the rules of logic.
Zero Information spontaneously turned into all information
We don’t have a single example in the history of science in which information has ever com from anything other than intelligence. There is no property of physics or chemistry that can account for the information we se in DNA.
Stephen C. Meyer; Philosopher of Science, Cambridge University
Challenge Question: If there has never been a single example of information coming from anything other than intelligence—is it reasonable to assume that the infinite amount of information contained in the Universe occurred spontaneously with perfect chemical, genetic, and biological and quantum precision?
Premise 3: Complex design cannot just occur randomly
ran·dom
Oxford Dictionary
/ˈrandəm/
adjective
1.
made, done, happening, or chosen without method or conscious decision.
While Charles Darwin was considered an expert in microscopy in his era, his achromatic microscope only had the power to examine specimens such as barnacles, plants, insects and their body parts. He had extremely limited knowledge of the cell and it’s components, and no knowledge of DNA. Throughout the 1800’s and even the early 1900’s cellular and organismic systems were considered simple biological systems that were for the most part fully understood.
Darwin did not know that genes existed, much less that genes are the mechanism by which an organism’s or plants traits, appearance, instincts and behaviors are passed on within a species.
Livescience.com (What is Darwin’s Theory of Evolution?)

The complexity of cells, DNA, molecules, and enzymes could not be observed or be documented before the electron microscope. Modern micro-biology has revealed that cellular systems while infinitesimally small, are infinitely complex.
Even the smallest bacterial cell, which weighs less than a trillionth of a gram, is “a veritable microminiaturized factory” containing thousands of exquisitely designed pieces of intricate molecular machinery, made up altogether of 100 thousand million atoms, far more complicated than any machine built by man and absolutely without parallel in the non-living world. Nearly every feature of our own advanced technology can be found in the cell
Micheal Denton, Evolution: A Theory in Crisis. Biochemistry Phd, King’s College London

In the book “What is a complex system?” asking three questions will help identify a complex system
- How difficult is it to describe?
- How difficult is it to create?
- How organized is it’s structure?
Here is what a minimal free-living cell (capable of using chemicals and energy obtained from its surrounding environment and reproduce) must have:
- A cell membrane. This separates the cell from the environment. It must be capable of maintaining a different chemical environment inside the cell compared to outside (as above). Without this, life’s chemical processes are not possible.
- A way of storing the information or specifications that instructs a cell how to make another cell and how to operate moment by moment. The only known means of doing this is DNA.
- A way of reading the information in order to make the cell’s components and also control the amount produced and the timing of production. The major components are proteins, which are strings (polymers) of hundreds to thousands of some 20 different amino acids.
Life is based on machines—machines made of molecules! Molecular machines haul cargo from one place in the cell to another along “highways” made of other molecules, while still others act as cables, ropes, and pulleys to hold the cell in shape. Machines turn cellular switches on and off, sometimes killing the cell or causing it to grow. Solar-powered machines capture the energy of photons and store it in chemicals. Electrical machines allow current to flow through nerves. Manufacturing machines build other molecular machines, as well as themselves. Cells swim using machines, copy themselves with machinery, ingest food with machinery. In short, highly sophisticated molecular machines control every cellular process. Thus the details of life are finely calibrated, and the machinery of life enormously complex.
Michael Behe; Darwin’s Black Box, The Biochemical Challenge to Evolution
A minimal cell needs several hundred complex proteins that would have had to evolve simultaneously for even one cell to survive for even one second. Each cell has a DNA strip that stores vast amounts of information pertinent to the cells function and survival. That DNA would have had to appear randomly in tact for even the simplest one-celled organism to survive even one second if evolution is true.
Assuming that the original primeval form of life was some kind of an ameoba—where did it obtain the almost infinite number of bits of information required to be stored in its DNA storage and retrieval system? In order to transform the ameoba type of cell to a mammal, a primate, an octopus, or a bee, new bits of holistic information are required. neither the primeval ameoba type of cell nor the inorganic matter of which it is constructed contains such highly specialized, holistic information which is necessary to transform the alleged ameoba into, say, an anthropoid ape.
Is it legitimate to assume that such incredible amounts of information arose spontaneously out of thin air by pure chance?
A.E. Wilder-Smith; PhD Physical Organic Chemistry, Phd Pharmacology
Challenge Question : If life is this complex at the most microscopic level how could it develop just by random chemistry and chance without intelligent design? How could every living thing have it’s own uninterchangeable DNA code through random chance?
Premise 4: Living organisms are irreducibly complex—at the anatomical, cellular, and molecular levels
irreducible
adjective
ir·re·duc·ible ˌir-i-ˈdü-sə-bəl
: impossible to transform into or restore to a desired or simpler condition
: impossible to make less or smaller
Irreducible complexity is a scientific phrase used to mean a single system which is composed of several interacting parts, where the removal of any one of the parts causes the whole system to cease functioning.
An automobile is an example of irreducible complexity. If you remove the starter, a single spark plug, fuel pump, or radiator hose it will not function. Biological and anatomical organs, cells, blood vessels etc. are even more irreducibly complex.
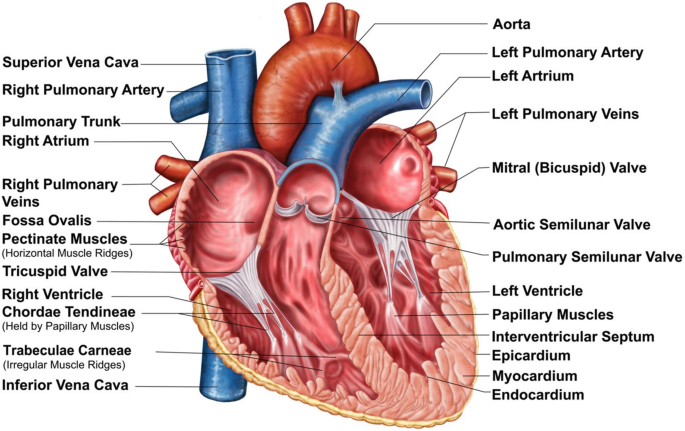
In Biology a heart, brain or eye are examples of irreducible complexity. If you remove any part of the heart —it can be an aorta, valve, artery, or membrane it will cause the heart to fail and die. The same follows with the cornea, iris, or retina.
The Theory of Evolution assumes that complex organs and organisms are built up by infinitesimally small inherited variations accumulated over millions of years.
The proposed order of Evolution of Organisms on Earth is as follows:
algae → invertebrates → vertebrates → amphibians → reptiles → mammals
The Theory of Evolution is based on two essential components:
- Random Variations: Organisms transform into more complex organisms through micro-mutations over extended periods of time
- Survival of The Fittest: The natural process by which organisms best at adapting to their environment and are most successful at reproducing survive.
As we saw when discussing the complexity of DNA—all organisms are incredibly complex even at the cellular level. The question that arises is—how could organisms survive while cells, organs, eyes, limbs and traits are being formed by infinitesimally small inherited variations over time?
- How could organisms function while the brain was only partially formed?
- How could organisms breath while the lungs only partially formed?
- How could organisms see while eyes ….
- How could blood circulate while vessels and arteries …
- How could organism process food while intestines, stomach, and bowels …
- How could organisms mobilize while appendages such as arms, wings, legs…
Human lungs are another great example of irreducible complexity. Here are the evolutionary steps Proof Of Evolution.com gives for how the human lung evolved from fish:
- Fish evolved the ability to use their swim bladder (a flotation device in fish containing air) to collect oxygen
- The swim bladder evolved ridges and undulations inside creating more surface area.
- The ridges and undulations enlarged and connected producing tubes.
“The only step left was a tube to the outside so the fish could breathe the air in“
proofofevolution.com
Remember it is widely accepted that even the smallest evolutionary changes (micro-mutations) take thousands to millions of years to to occur which is why we are supposedly unable to view evolution taking place in a laboratory or in the fossil record.
What Proof Of Evolution.Com can’t explain is how did the fish survive one generation to the other without all the parts essential for survival.
Another evolutionary claim is that the one-chambered heart pump evolved first, and then it evolved into the two-chambered heart, then the three-chambered heart, and finally, the four-chambered heart, which is used in all mammals. In short, evolution states that the circulatory system evolved from a simple system in bacteria to the complex system in humans by the natural selection of billions of micro-mutations which took millions of years.
There isn’t a single biological heart of any species that could with only partially developed valves, aorta, ventricles or septums. At the same time the heart was supposedly evolving blood, and the circulatory systems would have to go similar timely evolutionary advancement in order to accomodate the more sophisticated heart. The question is how would survive while their irreducibly complex systems were changing.
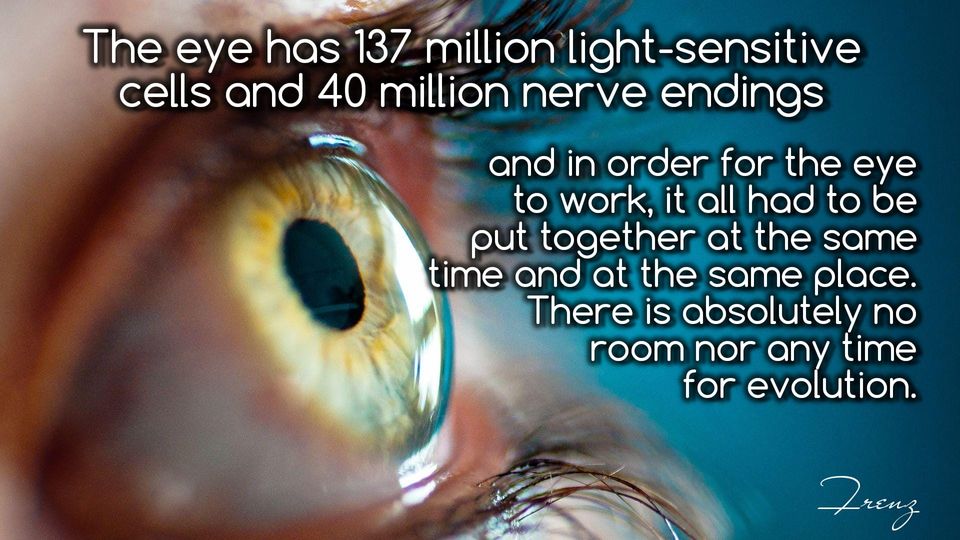
Concerning the irreducible complexity of the eye — British Journalist, and filmmaker. Author of The Neck of The Giraffe or Where Darwin Went Wrong wrote:
It is quite evident that if the slightest thing goes wrong en route—if the cornea is fuzzy, or the pupil fails to dilate, or the lens becomes opaque, or the focusing goes wrong—then a recognizable image is not formed. The eye either functions as a whole or not at all. So how did it come to evolve by slow, steady, infinitesimally small Darwinian improvements? Is it really plausible that thousands upon thousands of lucky chance mutations happened coincidentally so that the lens and the retina, which cannot work without each other, evolved in synchrony? What survival value can there be in an eye that doesn’t see?
To suppose that the eye with all its inimitable contrivances for
(Darwin C., “The Origin
adjusting the focus to different distances, for admitting different
amounts of light, and for the correction of spherical and chromatic
aberration, could have been formed by natural selection, seems, I
freely confess, absurd in the highest degree.”
” The eye to this day gives me a cold shudder”
of Species” Chapter on Organs Of Extreme Perfection and Complication
How survival fitness of organisms could remain unimpaired while while organisms are transitioning into other organisms with partially formed lungs, hearts, wings, tails, gills, and eyes is difficult if not impossible to imagine.
The Irreducible Complexity of vital organs and circulatory systems by which hearts, lungs, and brains are co-dependent would require them to formed all at once fully operational for biological fitness and reproduction to be possible at all.
“If it could be demonstrated that any complex organ existed which could not have been formed by numerous, successive, slight modifications, then my theory would absolutely break down.
Charles Darwin; The Origin of Species , Chapter on Organs of Extreme Perfection and Complication
Challenge Question : If evolution occurs by micro-mutations (small infinitesimal changes) occurring individually and sporadically over hundreds of thousands of years. How could complex organs like hearts, lungs, and eyes be able to function only partially formed until the rest of the needed micro-mutations arrived ?
ThinkCubed Truth Veracity Grid
Have I considered the issue carefully and honestly with an open mind?
Does what I think conform to the rules of logic and avoid contradictions?
Are my conclusions free from bias or presuppositions?

